Theoretical Approach to Probability
Theoretical Approach to Probability: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Experimental Probability Getting Closer to Theoretical Probability, Probability, Probability of an Event in an Experiment with Continuous Outcomes & Geometric Probability etc.
Important Questions on Theoretical Approach to Probability
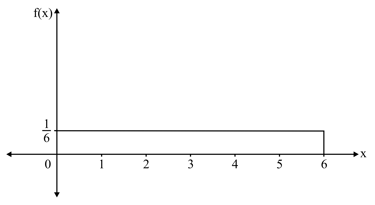
The probability of the function is .
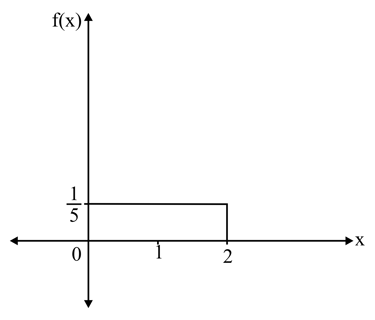
The probability of the function is unit.
The probability of any continuous function is calculated by calculating its _____
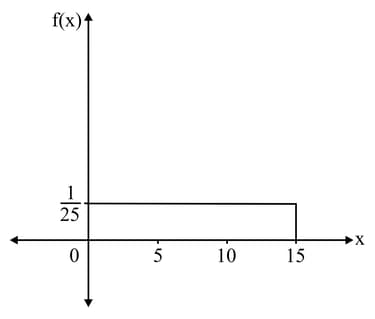
Calculate the probability of the function
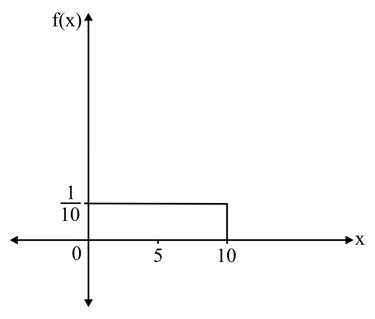
Calculate the probability of the function
Find the total number of elementary events associated with the random experiment of rolling a pair of dice together.
Find the total number of elementary events associated with the random experiment of tossing two coins.
Find the total number of elementary events when a coin is tossed.
A pair of dice is rolled.If the outcome is a doublet, a coin is tossed. Determine the total number of elementary events associated to this experiment.
What is the total number of elementary event associated to the random experiment of throwing three dice together?
An experiment was conducted times to find the number of instances for which an event occurred. If the event occurred times, find its Empirical Probability.
In a group of people, people chose to order non-veg burgers over the veg. What is the empirical probability of someone ordering veg burgers?
Two students and appeared in an examination. The probability that will qualify the examination is and that will qualify the examination is . The probability that both will qualify the examination is . Find the probability that at least one of and will not qualify (correct to decimal places).
There are two children in a family, the probability that both are girls is:
The probability of an event is greater than or equal to and less than or equal to _____ .
If and are mutually exclusive events and , then find .
All jacks, queens and kings are removed from a pack of cards. The remaining cards are well-shuffled and then a card is randomly drawn from it. Find the probability that this card is a red card.
If, what is the probability of 'not ' is .
The probability of selecting a red king from a deck of cards is _____.
In a game, the entry fee is . The game consists of tossing a coin times. If one or two heads show, Sweta gets her entry fee back. If she tosses heads, she receives double the entry fee. Otherwise, she will lose. For tossing a coin three times, If the probability that she receives double the entry fee is , then find the value of .
